Sustainability is increasingly more important to consumers. Companies worldwide are making changes to reduce their carbon footprint and leave a more positive impact on the planet to answer this growing concern. An important way companies can realize improved sustainable impact is through better product packaging practices.
When choosing packaging, there are many material choices, such as glass and various types of plastic. Both materials are available in many standard sizes and shapes, and both can be customized to a specific brands’ needs. However, if sustainability is important to your business, plastic offers significant advantages over glass in several key areas.
Continue reading or watch the video to learn more.

Plastic Offers Better Sustainability of Raw Materials
![]() Sustainable use of raw materials is one of the most recognized benefits of plastic. Like glass, plastic production relies on finite natural resources; however, compared to glass’ constant drain on raw materials, plastic offers unique benefits in recycled applications.
Sustainable use of raw materials is one of the most recognized benefits of plastic. Like glass, plastic production relies on finite natural resources; however, compared to glass’ constant drain on raw materials, plastic offers unique benefits in recycled applications.
The Glass Manufacturing Process
Manufacturing glass bottles can leave a large impact on the environment. Sand is the primary ingredient in glass. The sand is heated to an extremely high temperature, melted into a liquid state, and then used in molds to make bottles. Although it may seem like we have a readily accessible and abundant supply of sand, it’s actually being used faster than it can be naturally replenished. In addition, high silica sand is required to make glass. Sand with a high silica content is typically found in active or extinct riverbeds and sea beds. Removing this sand can have far reaching consequences.
Displacement of sand negatively affects many ecosystems. Sand removal can cause damage to surrounding habitats, disturb river flows, and cause lasting harm. In addition, removing sand from the sea bed also leaves shore communities prone to flooding and erosion. For these reasons, sand consumption is not the most sustainable or environmentally sound practice.
Plastic Uses Less Energy to Produce
![]()
Producing glass is an extremely heat-intensive process and uses a large amount of energy. The raw materials are placed in a furnace where they are heated to 2600 – 2800 degrees Fahrenheit for melting. The temperature is then reduced as the molten glass is cut, molded, and blown into its final bottle form. The glass making process requires energy that is equivalent to 3.0 grams of CO2 per 1.0 gram of glass.
The Plastic Manufacturing Process
On the other hand, producing plastic utilizes less energy. First, the hydrocarbon raw materials are polymerized into resin pellets using a reactor. Then the resin is shipped to a processor. At the processor, the resin is melted and blown into a mold to form the shape of a bottle using temperatures of 400 – 500 degrees Fahrenheit. The energy used to make and process plastic is equivalent to 3.8 grams of CO2 per 1.0 gram of plastic.
Consider this. More material is required to make glass bottles. For example, an 82.2 gram glass jar at 3.0 CO2 equivalents per gram has a total impact of 246.6 grams of CO2 equivalents per jar. A lighter 13.0 gram HDPE plastic jar with 3.8 CO2 equivalents per gram has a total impact of 49.4 grams of CO2 equivalents. The plastic jar has only 20% of the carbon impact of the glass jar. It would take 5 plastic jars to equal the environmental impact of just one glass jar. This demonstrates the full story when comparing the energy need to make glass versus plastic.
The CO2 savings is significant with plastic. Use the example of an order of 1,000,000 2 oz. jars. In this scenario, glass jars yield 246.6 Metric Tons of CO2, but plastic jars only yield 49.4 Metric Tons of CO2. The difference? Plastic yields a savings of 197.2 Metric Tons of CO2. To demonstrate in familiar terms, this savings is equivalent to the following everyday items.

Sustainable Plastic Resin Options

Most plastics (excluding bioplastics) are petroleum-based, relying on finite natural resources like oil and natural gas. Drilling for oil disturbs both the land and marine ecosystems.
Often, dealing with oil can result in oil spills, which contaminate soil and water, and may cause catastrophes such as fires and explosions. However, there are alternative sustainable options.
Resin Produced through Mechanical Recycling
One of the most common methods to recycle plastic waste is Mechanical Recycling. In this process, post-consumer plastic waste is sorted, washed, shredded, and heated back into plastic resin pellets with the actual molecular structure intact. This process requires raw material that is as clean and pure as possible.
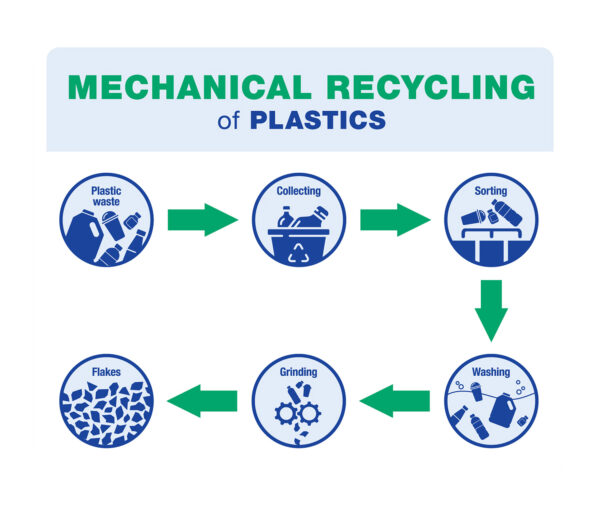 Only certain types of plastic waste can be used in this process. In addition, different colored plastics are used, so it’s likely that color will vary from batch to batch depending upon the pigmentation of the waste plastic used. Mechanically recycled plastic can only be reprocessed a limited number of times, and it loses physical properties each time it is processed.
Only certain types of plastic waste can be used in this process. In addition, different colored plastics are used, so it’s likely that color will vary from batch to batch depending upon the pigmentation of the waste plastic used. Mechanically recycled plastic can only be reprocessed a limited number of times, and it loses physical properties each time it is processed.
Mechanically recycled HDPE and PET help reduce greenhouse gas emissions that are damaging our planet. In a circular economy, making new products from plastic waste removes plastic from the environment by converting discarded plastic back into resin that can be used again. These resins are also fully recyclable in the current recycling stream.
Considering a switch from traditional plastic to a mechanically recycled plastic? You can calculate the environmental savings both options yield by using our PCR PET and PCR HDPE sustainability calculators.
If you currently utilize glass containers for your packaging, you can determine the savings when you switch from glass to traditional PET plastic, or from glass to traditional HDPE plastic. Try our Glass to PET Conversion Calculator and our Glass to HDPE Conversion Calculator on a typical packaging order and see how you can improve your carbon footprint and reduce your costs.
Virgin Resin Produced through Advanced Recycling
Advanced Recycling is the emerging sustainable method to obtain ethylene molecules needed to produce polyethylene. Post-consumer waste and several other feedstocks (specific chemical ingredients) are used to generate identical ethylene molecules.

In addition, the Advanced Recycling process ensures that the resulting virgin resin is identical to virgin resin produced with fossil fuels, like oil and natural gas. Like all virgin resins, resin produced through the Advanced Recycling process is free from foreign material and other contaminants. Learn more.
Plastic Uses Less Energy to Transport
![]() Glass is very fragile and needs extra packaging during transport to keep it from cracking or breaking. In turn, a trailer can carry a greater number of plastic bottles because they use less packaging which takes up less space.
Glass is very fragile and needs extra packaging during transport to keep it from cracking or breaking. In turn, a trailer can carry a greater number of plastic bottles because they use less packaging which takes up less space.
When glass or plastic bottles are produced and ready for distribution, it still takes more fuel to transport glass products the same distance as plastic products because glass is heavier. A greater negative impact on the environment results from using more fuel means greater carbon emissions.
Understand the Differences and Help Save the Planet
Only you can determine whether glass or plastic is best for your product. However, if reducing your carbon footprint is a high priority, plastic has distinct advantages over glass. You can make more informed decisions about your packaging options when you understand these differences.
At Drug Plastics, we invest in our customers’ success and value our partnerships. When you work with us, we provide you with all the information you need to make decisions that improve your sustainability, increase your bottom line, and improve your brand.
For more information, speak with someone immediately at 610-367-5000.