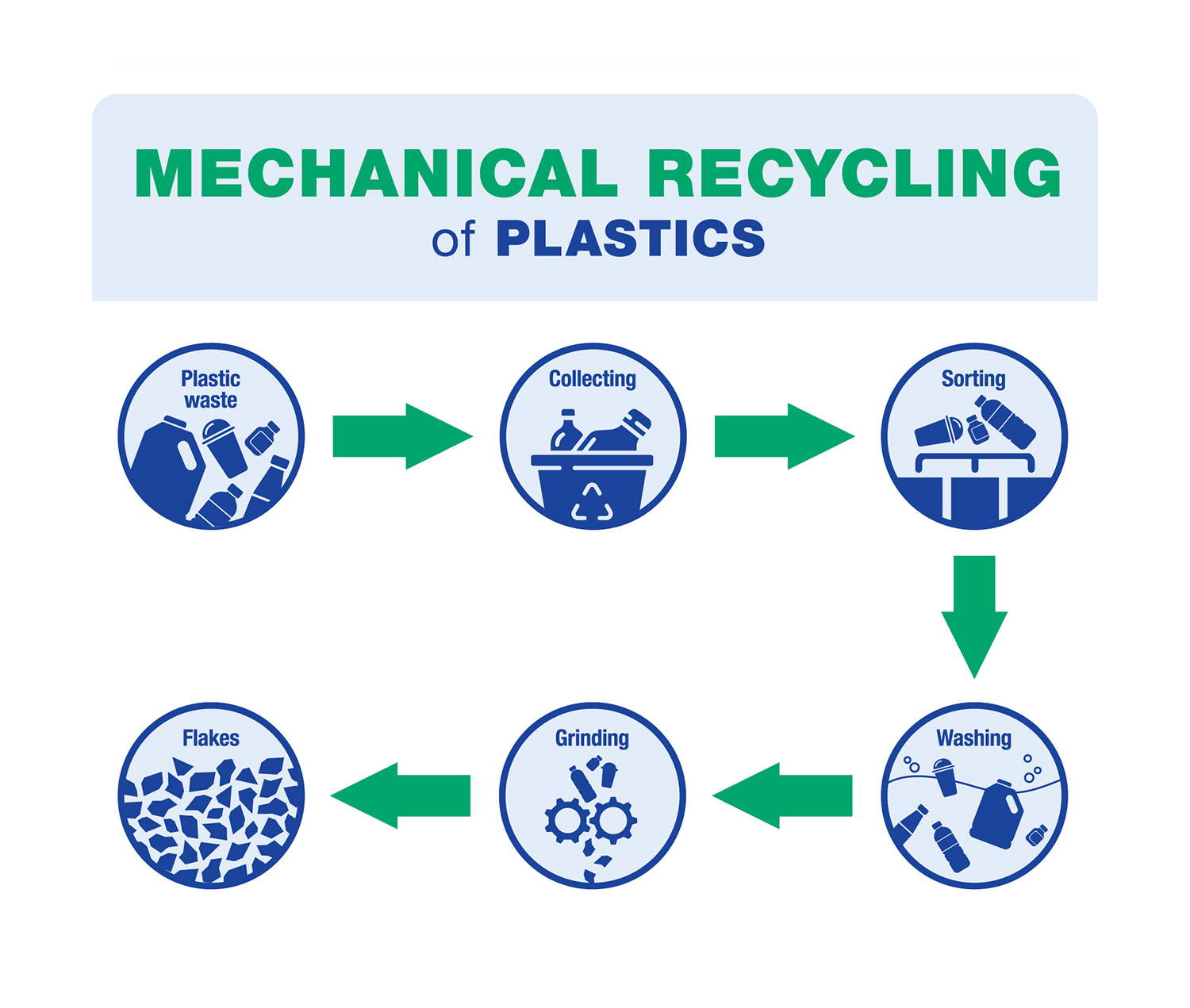
The Mechanical Recycling Process
One of the most common methods to recycle plastic waste is Mechanical Recycling.
In this process, post-consumer plastic waste is sorted, washed, shredded, and heated back into plastic resin pellets with the actual molecular structure intact. Mechanical Recycling requires raw material that is as clean and pure as possible.
Only certain types of plastic waste can be used. In addition, it’s likely that color will vary from batch to batch depending upon the pigmentation of the plastic waste.
Mechanically recycled plastic can be reprocessed a limited number of times, and loses physical properties each time.
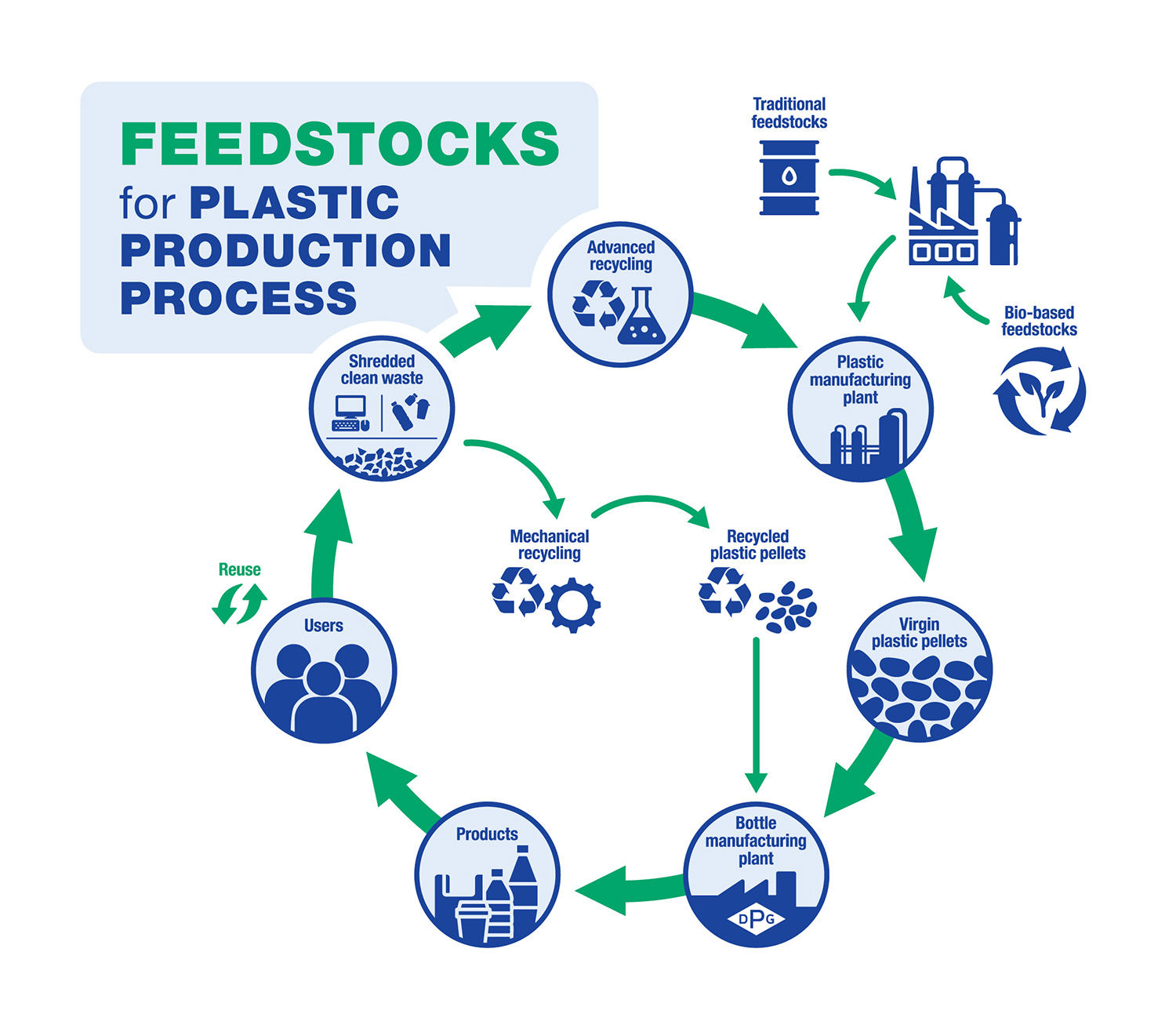
This graphic shows the Mechanical Recycling process as well as the three other polyethylene resin production processes:
- Virgin resin production from fossil fuels
- Virgin resin produced through the Advanced Recycling process
- Virgin resin production using bio-based feedstocks
Making new plastic products with resin made from post-consumer recycled (PCR) waste is more efficient in terms of greenhouse gas emissions than manufacturing those same products with virgin plastic resin.
Producing recycled products yields an increased energy savings versus producing virgin products.
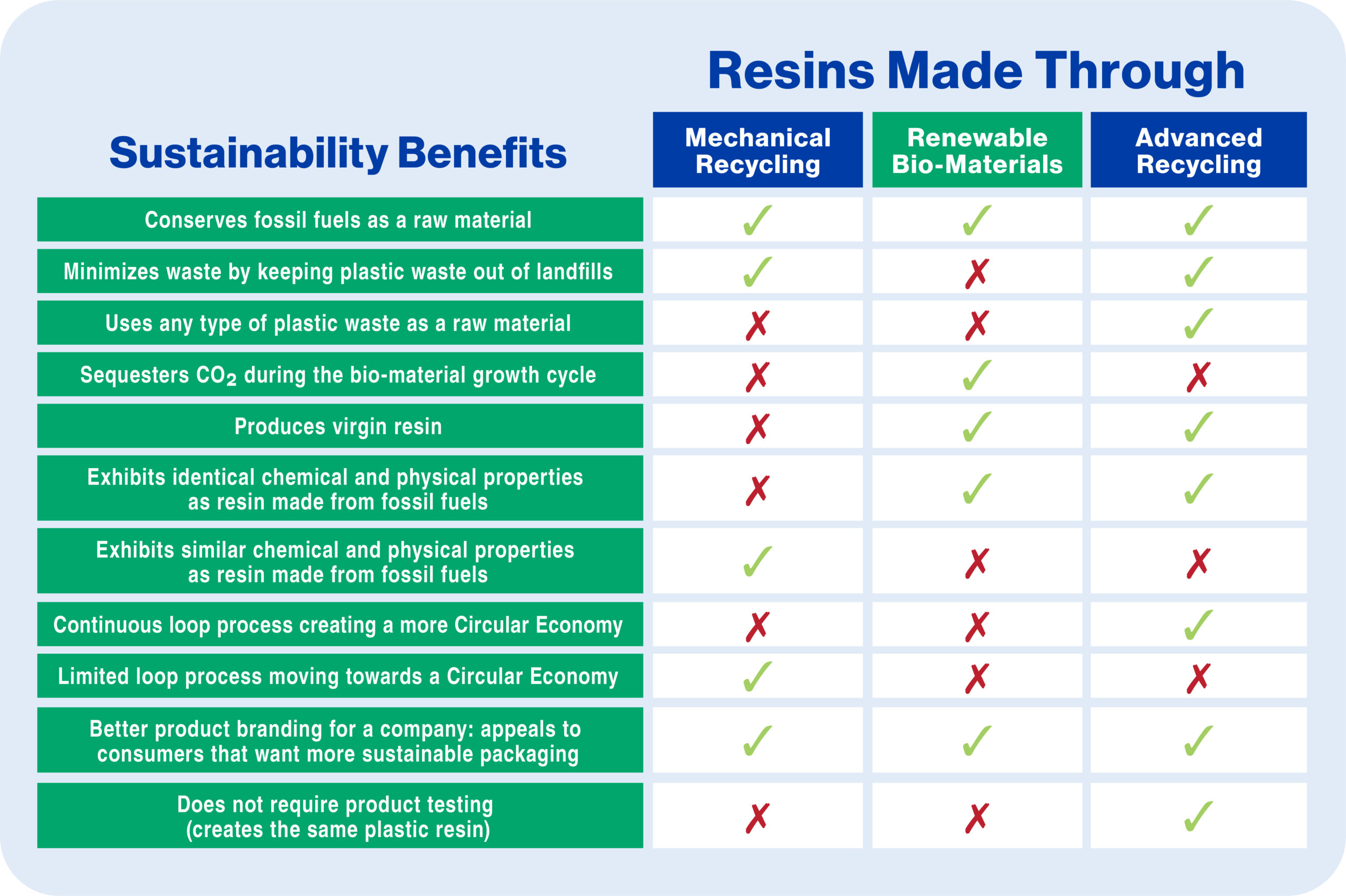
How to Choose
Notable differences exist between resin types and there’s much to consider during the product packaging design process.
If you want to minimize waste by keeping plastic waste out of landfills, and appeal to consumers who want more sustainable packaging, resins made through Mechanical Recycling may be the right option. We’ve outlined the benefits of each resin type so you have the information you need to make the right decision.
Want to learn more about how plastic packaging produced with mechanically recycled resin can help to reduce your carbon footprint?
Read the article and see how simple changes can have a lasting impact on the environment.

Contact Us for More Information
